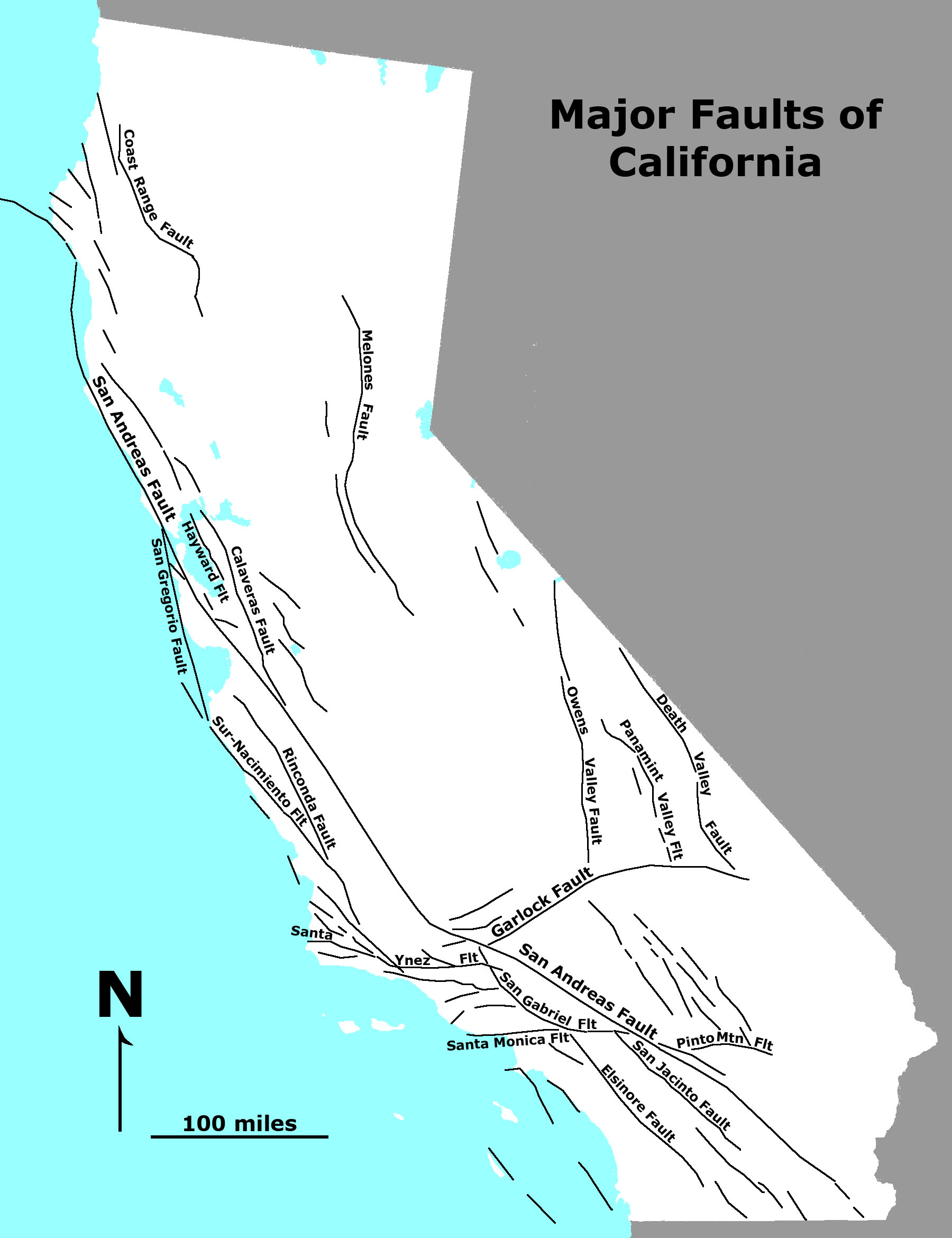
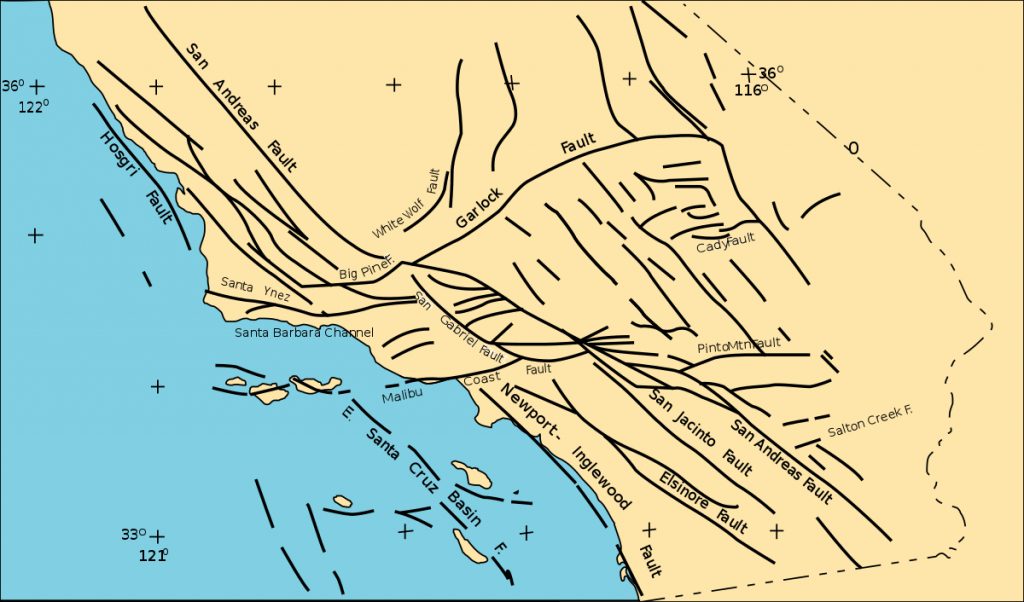
California, a state renowned for its natural beauty and vibrant culture, is also infamous for its complex network of fault lines. These geological features are not just fascinating to study but also pose significant risks to millions of residents. Understanding California fault lines is crucial for anyone living in or visiting the region, as it can help prepare for potential earthquakes and their consequences.
Earthquakes are a natural phenomenon that has shaped California's landscape over millions of years. The state's fault lines are the result of tectonic activity, where massive plates beneath the Earth's surface move and interact. This movement creates energy that is released in the form of seismic waves, causing earthquakes. By exploring the science behind these fault lines, we can better understand their impact on communities and infrastructure.
This article delves into the intricacies of California fault lines, offering insights into their formation, significance, and the measures being taken to mitigate their effects. Whether you're a geology enthusiast, a homeowner, or simply curious about the forces shaping our planet, this comprehensive guide will provide valuable information to help you stay informed and prepared.
Read also:Desi Forum A Comprehensive Guide To Understanding And Maximizing Its Potential
Table of Contents:
- Introduction to Fault Lines
- California Fault Lines Overview
- San Andreas Fault: The Most Famous Fault
- Other Major Faults in California
- Earthquake Activity in California
- Risks and Impact of Fault Lines
- Mitigation Strategies for Earthquakes
- Technology and Research in Seismology
- Historical Earthquakes in California
- Future Predictions and Preparedness
- Conclusion
Introduction to Fault Lines
What Are Fault Lines?
Fault lines are fractures or zones of fractures between two blocks of rock. They occur when the Earth's crust moves due to tectonic forces, leading to the displacement of rock layers. In California, fault lines are particularly prominent due to the state's location along the boundary of the Pacific Plate and the North American Plate. These plates are constantly moving, creating stress that eventually results in earthquakes.
The study of fault lines is a critical aspect of geology, as it helps scientists predict seismic activity and understand the Earth's dynamic processes. By examining fault lines, researchers can identify areas prone to earthquakes and develop strategies to minimize damage and protect lives.
California Fault Lines Overview
California is home to an extensive network of fault lines, making it one of the most seismically active regions in the world. These fault lines are the result of the interaction between the Pacific Plate and the North American Plate, which move in opposite directions. This movement creates significant stress on the Earth's crust, leading to frequent earthquakes.
The most well-known fault line in California is the San Andreas Fault, but there are many others that contribute to the state's seismic activity. Understanding these fault lines is essential for assessing earthquake risks and implementing safety measures.
San Andreas Fault: The Most Famous Fault
The San Andreas Fault is perhaps the most famous fault line in the world, stretching approximately 800 miles through California. It marks the boundary between the Pacific Plate and the North American Plate and is responsible for some of the largest earthquakes in the state's history.
Read also:Burlington Wa Childrens Museum A Fun And Educational Destination For Families
Key Characteristics of the San Andreas Fault
- Length: Approximately 800 miles
- Location: Runs through much of California, including major cities like San Francisco and Los Angeles
- Type: Transform fault, meaning the plates slide past each other horizontally
- Historical Earthquakes: Responsible for the devastating 1906 San Francisco earthquake
Other Major Faults in California
Besides the San Andreas Fault, California is home to several other significant fault lines. These include the Hayward Fault, the San Jacinto Fault, and the Calaveras Fault, among others. Each of these fault lines poses unique risks and contributes to the state's overall seismic activity.
Hayward Fault
The Hayward Fault, located in the eastern part of the San Francisco Bay Area, is considered one of the most dangerous fault lines in California. It has a history of producing large earthquakes, and experts believe it is overdue for another significant event.
San Jacinto Fault
The San Jacinto Fault runs parallel to the San Andreas Fault and is responsible for numerous earthquakes in Southern California. It is part of the larger fault system that makes the region highly prone to seismic activity.
Earthquake Activity in California
California experiences thousands of earthquakes each year, although most are too small to be felt by humans. However, the state has also witnessed several catastrophic earthquakes that have caused significant damage and loss of life.
Scientists use seismographs to monitor earthquake activity and study fault lines. This data helps them understand the behavior of faults and predict future seismic events. By analyzing historical earthquake patterns, researchers can identify areas at high risk and develop strategies to mitigate potential damage.
Risks and Impact of Fault Lines
The presence of fault lines in California poses significant risks to its residents and infrastructure. Earthquakes can cause widespread destruction, disrupt essential services, and result in loss of life. Additionally, fault lines can impact the state's economy, as businesses and industries may suffer from damage to facilities and supply chains.
To address these risks, it is crucial to implement effective mitigation strategies and educate the public about earthquake preparedness. This includes reinforcing buildings to withstand seismic activity, developing early warning systems, and promoting awareness campaigns.
Mitigation Strategies for Earthquakes
Several strategies are employed to mitigate the impact of earthquakes in California. These include:
- Building Codes: Enforcing strict building codes ensures that structures can withstand seismic forces.
- Early Warning Systems: Advanced technology allows for early detection of earthquakes, providing valuable time for people to take protective actions.
- Public Education: Educating the public about earthquake preparedness and safety measures is essential for reducing casualties and damage.
- Infrastructure Upgrades: Reinforcing critical infrastructure, such as bridges and highways, enhances resilience to seismic events.
Technology and Research in Seismology
Advancements in technology have significantly improved our ability to study and predict earthquakes. Modern seismographs and GPS systems provide real-time data on fault line activity, enabling scientists to better understand seismic processes. Additionally, research into fault mechanics and earthquake dynamics continues to enhance our knowledge of these phenomena.
Collaboration between scientists, engineers, and policymakers is crucial for developing effective strategies to mitigate earthquake risks. By leveraging technology and research, we can improve our preparedness and response to seismic events.
Historical Earthquakes in California
California has a long history of significant earthquakes, each leaving a lasting impact on the state. Some of the most notable events include:
- The 1906 San Francisco Earthquake: One of the most devastating earthquakes in U.S. history, it caused widespread destruction and fires throughout the city.
- The 1989 Loma Prieta Earthquake: Occurring during the World Series, this earthquake caused significant damage in the San Francisco Bay Area.
- The 1994 Northridge Earthquake: Striking the Los Angeles area, it resulted in extensive property damage and fatalities.
Future Predictions and Preparedness
While scientists cannot predict earthquakes with certainty, they can estimate the likelihood of future events based on historical data and fault line activity. The "Big One," a hypothetical massive earthquake along the San Andreas Fault, is often discussed as an inevitable event. Preparing for such an occurrence requires ongoing efforts to enhance infrastructure, improve emergency response systems, and educate the public.
By staying informed and taking proactive measures, Californians can reduce the risks associated with fault lines and earthquakes. This includes developing personal emergency plans, securing household items, and participating in community preparedness initiatives.
Conclusion
California fault lines are a fascinating yet formidable aspect of the state's geological landscape. Understanding these fault lines and their associated risks is essential for ensuring the safety and resilience of communities. Through advancements in technology, research, and mitigation strategies, we can better prepare for and respond to seismic events.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences regarding California fault lines in the comments below. Additionally, feel free to explore other articles on our site for more insights into geology and natural phenomena. Together, we can foster a culture of preparedness and resilience in the face of nature's challenges.