Capital gains tax on house sale in Colorado is a critical consideration for homeowners who are planning to sell their property. Whether you're a first-time seller or a seasoned real estate investor, understanding how capital gains tax works can help you make informed financial decisions. This tax applies to the profit you earn from selling your home, and it's essential to know the rules to avoid unexpected financial burdens.
In this article, we will explore the ins and outs of capital gains tax on house sales in Colorado, including exemptions, calculations, and strategies to minimize your tax liability. By the end, you'll have a clear understanding of how this tax affects you and how to navigate it effectively.
As a homeowner, being aware of tax obligations is crucial, especially when it comes to significant financial transactions like selling a house. This guide will provide you with all the necessary information to ensure you're well-prepared and compliant with Colorado's tax laws.
Read also:Discover The Excitement At Sunset Station Casino Henderson Nevada A Complete Guide
Table of Contents
- What is Capital Gains Tax?
- How Capital Gains Tax Works in Colorado
- Calculating Capital Gains Tax
- Exemptions and Deductions
- Federal vs. State Tax
- Strategies to Reduce Tax Liability
- Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Tax Filing Process
- Real Estate Market in Colorado
- Final Thoughts
What is Capital Gains Tax?
Capital gains tax refers to the tax levied on the profit earned from the sale of an asset, such as a house. In the context of capital gains tax on house sale in Colorado, this tax applies to the difference between the selling price of your home and its original purchase price, minus any improvements or expenses associated with the sale.
Key Points:
- Capital gains tax is only applied to the profit, not the entire sale price.
- Both federal and state governments may impose capital gains tax, depending on the jurisdiction.
- There are exemptions available for primary residences, which can significantly reduce your tax liability.
Types of Capital Gains
Capital gains can be classified into two categories: short-term and long-term. Short-term capital gains apply to assets held for less than a year, while long-term capital gains apply to assets held for more than a year. In Colorado, long-term capital gains typically receive more favorable tax treatment.
How Capital Gains Tax Works in Colorado
In Colorado, the capital gains tax on house sale is calculated based on the state's flat income tax rate, which is currently 4.55%. This rate applies to both short-term and long-term capital gains. However, it's important to note that federal taxes may also apply, depending on your income level and the amount of profit you make from the sale.
Factors Affecting Capital Gains Tax:
- Length of time you owned the property
- Whether the property was your primary residence
- Your annual income
- Improvements made to the property
Colorado's Unique Tax Structure
Colorado's flat tax rate simplifies the calculation of capital gains tax compared to other states with progressive tax systems. However, homeowners must still consider federal tax implications, which can vary significantly based on individual circumstances.
Read also:Aisha Sofey The Rising Star In The World Of Education And Digital Innovation
Calculating Capital Gains Tax
Calculating capital gains tax involves determining the adjusted basis of your property and subtracting it from the selling price. The adjusted basis includes the original purchase price, any improvements made to the property, and selling expenses.
Formula:
- Selling Price - Adjusted Basis = Capital Gains
For example, if you purchased a home for $300,000, made $50,000 in improvements, and sold it for $500,000, your capital gains would be calculated as follows:
Selling Price: $500,000
Adjusted Basis: $300,000 (purchase price) + $50,000 (improvements) = $350,000
Capital Gains: $500,000 - $350,000 = $150,000
Common Adjustments to Consider
When calculating your adjusted basis, consider the following adjustments:
- Home improvements (e.g., kitchen renovations, roof replacements)
- Selling expenses (e.g., real estate agent fees, closing costs)
- Property taxes paid
Exemptions and Deductions
One of the most significant exemptions for capital gains tax on house sale in Colorado is the primary residence exclusion. Under federal law, single filers can exclude up to $250,000 of capital gains, while married couples filing jointly can exclude up to $500,000. To qualify for this exclusion, you must have owned and lived in the home as your primary residence for at least two out of the five years leading up to the sale.
Other Potential Deductions:
- Medical expenses related to home modifications
- Losses from natural disasters
- Business use of home (if applicable)
Eligibility for Exemptions
To qualify for the primary residence exclusion, homeowners must meet specific ownership and use tests. These tests ensure that the property was used as a primary residence for a significant period, preventing abuse of the exemption by investors or vacation homeowners.
Federal vs. State Tax
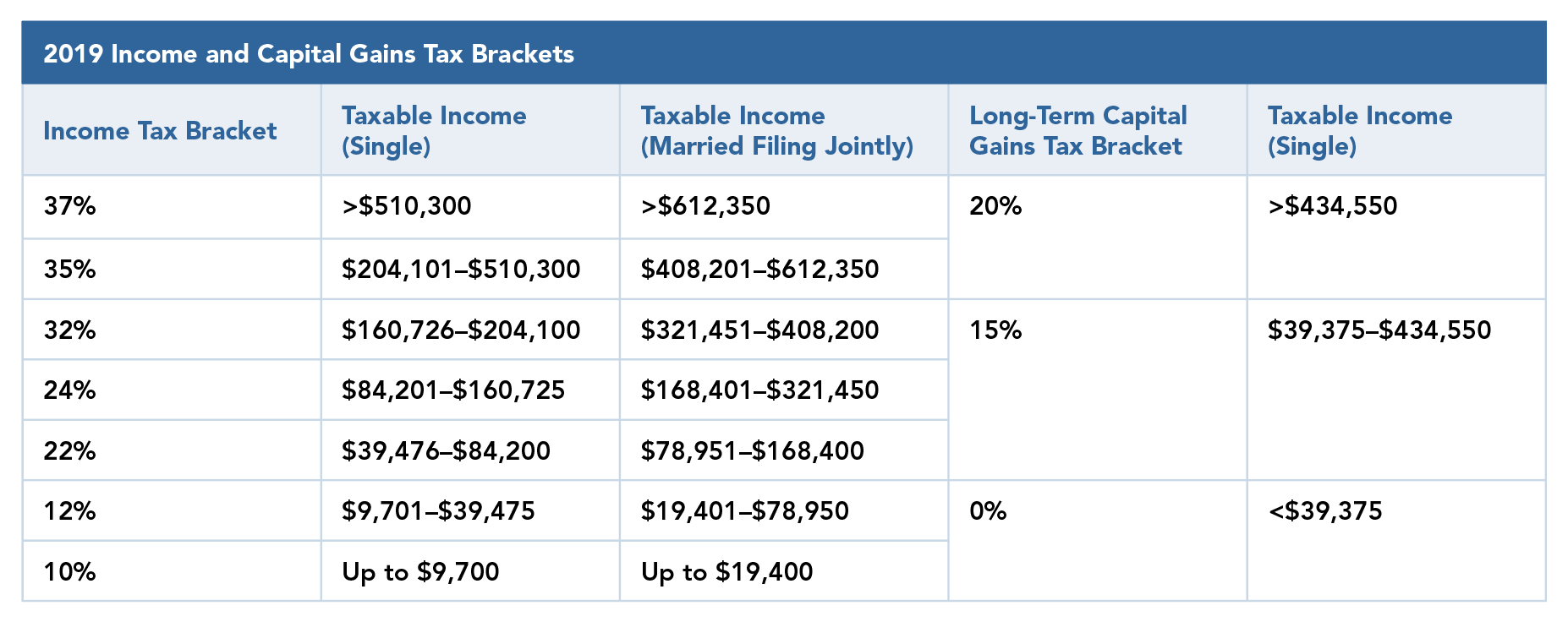
While Colorado imposes a flat tax rate of 4.55% on capital gains, federal tax rates can vary depending on your income level. For long-term capital gains, federal rates range from 0% to 20%, depending on your taxable income. Homeowners in Colorado must calculate both federal and state taxes to determine their total liability.
Comparison of Tax Rates:
- Colorado: 4.55% flat rate
- Federal: 0% to 20% (long-term), 10% to 37% (short-term)
Coordination of Federal and State Taxes
It's crucial to coordinate federal and state tax obligations to avoid overpayment or underpayment. Consulting with a tax professional can help ensure compliance with both jurisdictions and optimize your tax strategy.
Strategies to Reduce Tax Liability
Several strategies can help reduce your capital gains tax liability when selling a house in Colorado:
1. Timing Your Sale:
- Consider selling during a year when your income is lower to take advantage of lower tax brackets.
2. Maximizing Deductions:
- Document all improvements and expenses to increase your adjusted basis and reduce capital gains.
3. Utilizing Exemptions:
- Ensure you meet the eligibility requirements for the primary residence exclusion to maximize your tax savings.
Long-Term Planning
For homeowners planning to sell in the future, long-term planning can significantly reduce tax liability. Consider holding the property for more than a year to qualify for long-term capital gains rates and make strategic improvements that increase the property's value while minimizing taxable gains.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Mistakes in calculating or reporting capital gains can lead to unnecessary tax burdens or penalties. Here are some common mistakes to avoid:
- Underestimating selling expenses
- Forgetting to account for home improvements
- Not meeting the primary residence exclusion requirements
- Failing to file necessary tax forms
Importance of Accurate Record Keeping
Maintaining accurate records of all property-related expenses and improvements is essential for correctly calculating capital gains tax. Without proper documentation, you may miss out on potential deductions or face scrutiny during an audit.
Tax Filing Process
When filing taxes related to the sale of your home, you'll need to complete IRS Form 8949 and Schedule D to report capital gains or losses. Additionally, you may need to file a state tax return in Colorado to report your state-specific capital gains tax liability.
Steps to File:
- Gather all necessary documentation (e.g., closing statements, improvement receipts)
- Complete IRS Form 8949 and Schedule D
- File your federal and state tax returns by the deadline
Consulting a Tax Professional
Given the complexity of tax laws, consulting a tax professional can help ensure accuracy and compliance. A qualified accountant or tax advisor can guide you through the filing process and identify opportunities for tax savings.
Real Estate Market in Colorado
The real estate market in Colorado has been thriving in recent years, with home prices increasing significantly in many areas. This growth has led to substantial profits for homeowners selling their properties, making understanding capital gains tax more important than ever.
Market Trends:
- Rising home values in urban areas like Denver and Boulder
- Increased demand for suburban and rural properties
- Competitive bidding wars driving prices higher
Impact on Capital Gains
The booming real estate market in Colorado can result in higher capital gains for sellers, emphasizing the need for thorough tax planning. Homeowners should stay informed about market trends and consult with real estate professionals to make strategic decisions.
Final Thoughts
Understanding capital gains tax on house sale in Colorado is essential for anyone planning to sell their property. By familiarizing yourself with the tax rules, exemptions, and strategies to minimize liability, you can make informed decisions that protect your financial interests.
We encourage you to take action by reviewing your property records, consulting with a tax professional, and planning for your sale. If you found this article helpful, please share it with others who may benefit from the information. Additionally, feel free to leave a comment or question below, and we'll be happy to assist you further.
Remember, staying informed and proactive is the key to navigating the complexities of capital gains tax successfully.