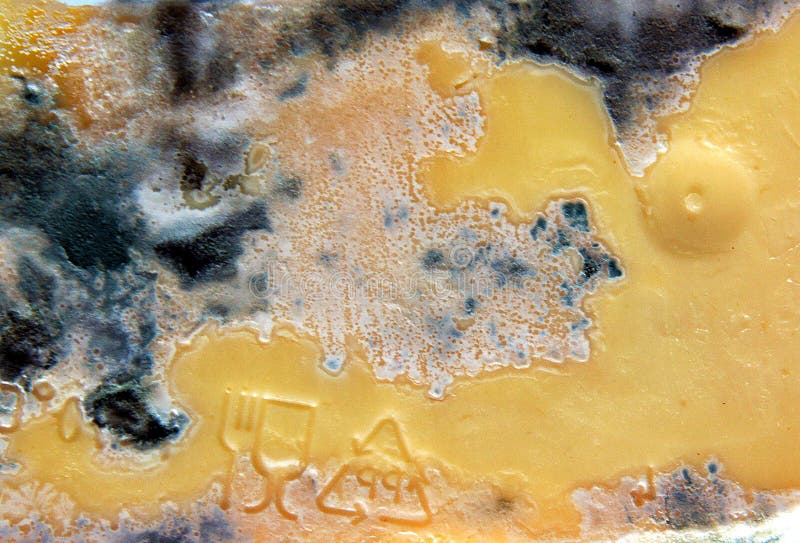
Cheese is one of the most beloved dairy products worldwide, but it can go bad if not stored properly. Spoiled cheese not only affects its taste but can also pose health risks. Learning how to identify signs of spoilage and understanding proper storage techniques is essential for cheese enthusiasts and households alike.
Many people are unsure about when cheese is considered spoiled and how to handle it safely. This article will delve into everything you need to know about spoiled cheese, including signs of spoilage, storage tips, and how to prevent waste. Whether you're a casual cheese consumer or a connoisseur, this information will help you make informed decisions about your cheese.
We will explore common questions about cheese spoilage, provide actionable tips, and ensure you have the knowledge to enjoy cheese safely and confidently. Let's dive into the world of cheese and learn how to preserve its quality and flavor.
Read also:Isaac Gordon Raymond A Comprehensive Exploration Of His Life Achievements And Legacy
Table of Contents
- Biography of Cheese
- Recognizing Spoiled Cheese
- Common Signs of Cheese Spoilage
- Preventing Cheese Spoilage
- Proper Cheese Storage Techniques
- Health Risks of Consuming Spoiled Cheese
- How Different Types of Cheese Spoil
- Frequently Asked Questions About Spoiled Cheese
- Can You Save Spoiled Cheese?
- Conclusion and Final Tips
Biography of Cheese
Cheese has a rich history that dates back thousands of years. Archaeological evidence suggests that cheese production began around 8,000 BCE in the Middle East. Over time, different cultures developed unique cheese varieties, each with distinct flavors, textures, and characteristics.
In this section, we'll explore the origins of cheese, how it's made, and the factors that contribute to spoilage. Understanding the biology of cheese helps in recognizing when it goes bad and how to extend its shelf life.
Types of Cheese
Cheese comes in various forms, from soft and creamy to hard and aged. The type of cheese affects how quickly it spoils. Below is a breakdown of common cheese types:
- Soft cheeses: Examples include Brie and Camembert.
- Semi-soft cheeses: Such as Gouda and Monterey Jack.
- Hard cheeses: Like Cheddar and Parmesan.
Recognizing Spoiled Cheese
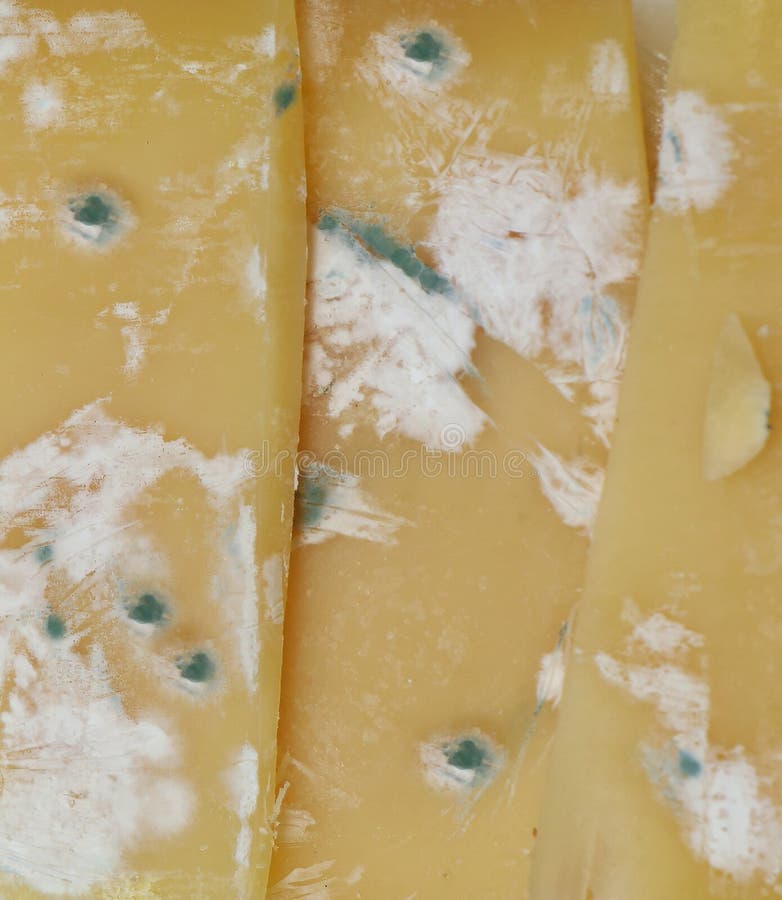
Recognizing spoiled cheese is crucial for maintaining food safety. Spoilage occurs when bacteria, mold, or yeast grow on cheese, altering its flavor, texture, and aroma. While some molds are safe and even desirable in certain cheeses, others can be harmful.
Visual Cues
Look for the following signs:
- Discoloration: A change in color, such as green or black spots.
- Mold growth: Unusual mold that doesn't belong to the cheese's natural characteristics.
- Slime formation: A slimy texture on the surface.
Common Signs of Cheese Spoilage
In addition to visual cues, other indicators can help determine if cheese has spoiled. These include:
Read also:Discover The Magic Of Aditi Mistri Videos Your Ultimate Guide
Smell
A spoiled cheese often emits a strong, unpleasant odor. If the smell is off-putting or significantly different from its usual aroma, it's best to discard it.
Taste
Although not recommended, tasting a small amount of cheese can help identify spoilage. If the flavor is sour, bitter, or off-putting, the cheese is likely spoiled.
Preventing Cheese Spoilage
Preventing cheese spoilage involves proper handling, storage, and understanding the specific needs of different cheese types. Below are some effective strategies:
Proper Handling
- Always use clean utensils when handling cheese.
- Refrigerate cheese promptly after opening.
Storage Containers
Using appropriate storage containers can significantly extend the shelf life of cheese. Consider wrapping cheese in wax paper or using airtight containers to maintain freshness.
Proper Cheese Storage Techniques
Proper storage is key to preserving cheese quality. Here are some tips:
Temperature Control
Cheese should be stored at temperatures between 35°F and 45°F (1°C to 7°C). Avoid exposing cheese to temperature fluctuations, as this can accelerate spoilage.
Humidity Levels
Humidity plays a critical role in cheese preservation. Soft cheeses require higher humidity levels, while hard cheeses prefer drier environments. Adjust storage conditions accordingly.
Health Risks of Consuming Spoiled Cheese
Consuming spoiled cheese can lead to foodborne illnesses. Common pathogens include:
Listeria
Listeria monocytogenes is a bacterium that can survive refrigeration and cause severe illness, especially in vulnerable populations such as pregnant women, elderly individuals, and those with weakened immune systems.
Salmonella
Salmonella contamination can occur if cheese is made from unpasteurized milk or improperly handled during production.
How Different Types of Cheese Spoil
Each type of cheese has unique characteristics that affect its spoilage rate. Below are some examples:
Soft Cheeses
Soft cheeses spoil faster due to their high moisture content. They are more susceptible to mold and bacterial growth.
Hard Cheeses
Hard cheeses are more resilient and can last longer when stored correctly. However, they can still develop mold or become dry and brittle over time.
Frequently Asked Questions About Spoiled Cheese
Here are answers to common questions about cheese spoilage:
Can You Eat Moldy Cheese?
It depends on the type of cheese. For hard cheeses, you can cut away the moldy portion and consume the rest. However, soft cheeses with mold should be discarded.
How Long Does Cheese Last?
The shelf life of cheese varies depending on the type and storage conditions. Unopened cheese typically lasts longer than opened cheese.
Can You Save Spoiled Cheese?
In some cases, you can salvage cheese that has started to spoil. For example, if only a small portion is affected, you can cut it away and use the rest. However, if the entire cheese is compromised, it's best to discard it to avoid health risks.
Conclusion and Final Tips
Cheese is a versatile and delicious food, but proper care is necessary to prevent spoilage. By understanding the signs of spoilage, practicing proper storage techniques, and being aware of health risks, you can enjoy cheese safely and minimize waste.
We encourage you to share this article with fellow cheese lovers and leave a comment below if you have any questions or tips of your own. Stay informed and keep your cheese fresh!
Data Source: USDA Food Safety Guidelines, FDA Cheese Safety Reports